|
Analysis
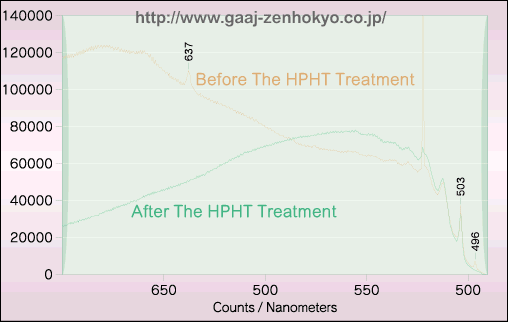
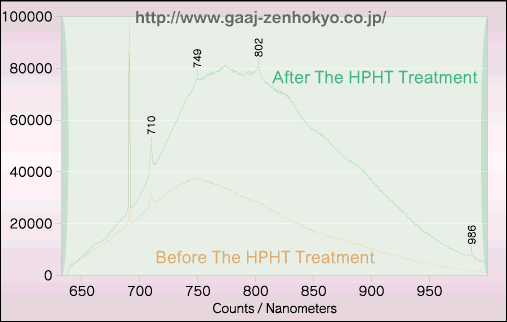
As with typeIIb brown diamonds above, they were examined by PL analysis using microscopic Raman spectroscope. The 488nm argon laser and the 633nm argon laser were used as exciting lasers. In the analysis using the 488nm laser, a peak at 496nm so called H4 centre disappeared after the treatment in both samples (figure 2), while (negatively charged H3 referred to as the H2) H2 peak at 986nm emerged in both samples after the treatment in the test using the 633nm laser (figure 3).
Conclusion In our experiment on HPHT treatment it was confirmed that brown was eliminated from typeIIb diamond and colour was deepened in typeIa diamond. Observation of external and internal features can reveal after-treatment characters such as blackening in cleavage, but not all diamonds show this character, and consequently PL analysis is the most effective method to distinguish natural or treated stones. The necessity of this analysis is heighten especially for typeIa diamond that is showing 1480cm-1 absorption, because this material is difficult to detect HPHT treatment in comparing with common typeIa diamond as typified by NOVA diamonds. |
||||||||
|