|
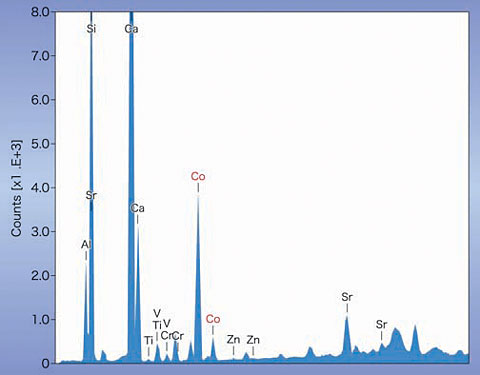
??Secondly, EDXRF (X-ray fluorescent analysis instrument) measured the sample. In the result, only common composition of zoisite was detected on the table facet, while Co was detected on the pavilion facets (figure 5). This means that the coating treatment covers only the pavilion facets with a layer containing Co as a colouring agent.
 |
|
fig-5:
|
EDXRF analysis results on pavilion facets of the coated zoisite;
cobalt (Co) is detected
|
|
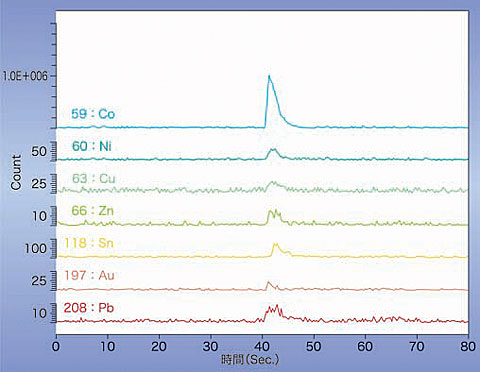
??LA-ICP-MS (laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry) analysis on the material was also reported in the paper of McClure and Shen (2008), which stated that elements such as Zn, Sn or Pb were detected beside Co mentioned above. GAAJ-ZENHOKYO Laboratory performed further detailed analysis with LA-ICP-MS, which detected elements such as Ni, Cu or Au in high contents next to Co, other than the elements mentioned above in the report of McClure and Shen (2008) (figure 6).
 |
|
fig-6:
|
LA-ICP-MS analysis results on pavilion facets of the coated zoisite
|
|
??Durability of the coating was reviewed in the report of McClure and Shen (2008). It specifies that they were unable to scratch the coating with a pin but a knife of hardened chrome steel could make a scratch. The sample we obtained did not show peeling by wiping off with alcohol or ultrasonic cleaning, but it was confirmed that flaws were caused to the coating layer when scratched by a blade of metal such as a cutter knife.
??From the results above, analysis by GAAJ-ZENHOKYO Laboratory corresponded to the observation by AGTA-GTC and GIA previously presented. The coating treatment itself is not a new one, but zoisite dealers should be alerted to the possibility of the coated material coming into circulation in the Japanese gem market in the near future.
※The coated zoisite submitted to our laboratory will be described on a gem identification report as below;
| Species |
Natural zoisite |
| Variety |
Zoisite |
| Comments |
Zoisite is commonly heated, but this process is not always determinable.
The stone is coated. |
|
Reference:
1) AGTA-GTC and AGL identify coated tanzanite (2008) Press release, May 23, http://www.agta-gtc.org/coated-tazanite.htm.
2) Shane F. McClure (2008) From GIA Research: Large coated tanzanites lack typical identifying features. GIA Insider, Vol.10, No,10 June 6, http://app.e2ma.net/campaign/35e913c2819a961cf9503f041f293eb6#article2.
3) AGT Gem Laboratory (2008) identification of coated tanzanite by observation with microscope, http://www.agt.jp/labnote/coated_tanzanite.shtml
4) Shane F. McClure and Andy H.Shen (2008) Coated Tanzanite. Gems & Gemology, Vol44, No.2. pp.142-147.
5) Andy H.shen, Wuyi Wang, Matthew S. Hall, Steven Novak, Shane F. McClure, James E. Shigley, and Thomas M. Moses (2007) Serenity coated colored diamonds: detection and durability. Gems & Gemology, Vol43, No.1. pp.16-34.
6) Coated natural topaz(1997)Masahiko Hayashi.Journal of the Gemmological Society of Japan Vol.22, No.1-4. pp.33.
7) A gathering with Dr. Balitsky, “Coated Topaz”(2001)GEMMOLOGY Vol.XXXⅡ, No.385. pp.14-15.
8) Schmetzer, K. (2006) Surface coating of gemstones, especially topaz - a review of recent patent literature. Journal of Gemmology, Vol.30, 1/2, pp.83-90. |

